Where’s the pipeline? Tokyo Prime-listed companies goal of 30% female board members
The Japanese government has set a goal for Prime-listed companies on the Tokyo Stock Exchange of each having at least one female board member by 2025. The aim is to have at least 30 percent of board members be women by 2030. By the end of July 2022, only 11.4% of all companies listed on the Prime List of the Tokyo Stock Exchange had women on their boards compared to 45% of equivalent companies in France and 31% in the United States.
This has prompted an outbreak of appointments of women to company boards during this summer’s shareholder meetings, mostly to non-executive directorships. Many of the new women board members do not have direct corporate line management experience, and are lawyers, accountants, academics and journalists. Even then, the scarcity of suitable women has meant a far higher proportion of the women have multiple non-executive directorships, compared to male board directors. Japan’s Financial Services Authority has pointed out that the goal of 30% by 2030 is not to have 30% of board members as external female directors, rather that Japanese companies should be planning now on how to have a pipeline by 2030 of suitable internal female candidates.
Japanese companies are going to struggle with this. One Japanese local bank stated that while 45% of its new graduate entry hires were female, only 6% of its managers were female. Another Japanese business organisation head said “there are no [suitable female] candidates” for the board. But as the Nikkei pointed out, the question is whether there really are none, or that women employees are just not being groomed for the board.
The motivation to change should not just be about caving into government pressure. According to JP Morgan Securities, their stock index compiled of companies with a high proportion of female executives started to outperform the TOPIX 500 in 2020, when the COVID pandemic started. Nishihara Rie, chief equity strategist at JPMorgan Securities, said, “During a crisis like the COVID, investors look more closely at the quality of management and the board of directors. Having women on the management team was seen as a factor in positively evaluating the board.”
Having people without mainstream corporate line management experience on the board is of course itself a sign of diversity and inclusion, and brings a fresh perspective to Japanese companies with long traditions of life time employment and seniority based promotion. But of course if only women from outside the company are appointed to the board, then there is a lack of role models for women employees in the company. Also, women from outside the company will not have the power base and influence within the company that internally appointed men have. I’m not sure 7 years is long enough for Japanese companies to fix this.
For more content like this, subscribe to the free Rudlin Consulting Newsletter. 最新の在欧日系企業の状況については無料の月刊Rudlin Consulting ニューズレターにご登録ください。
Read More
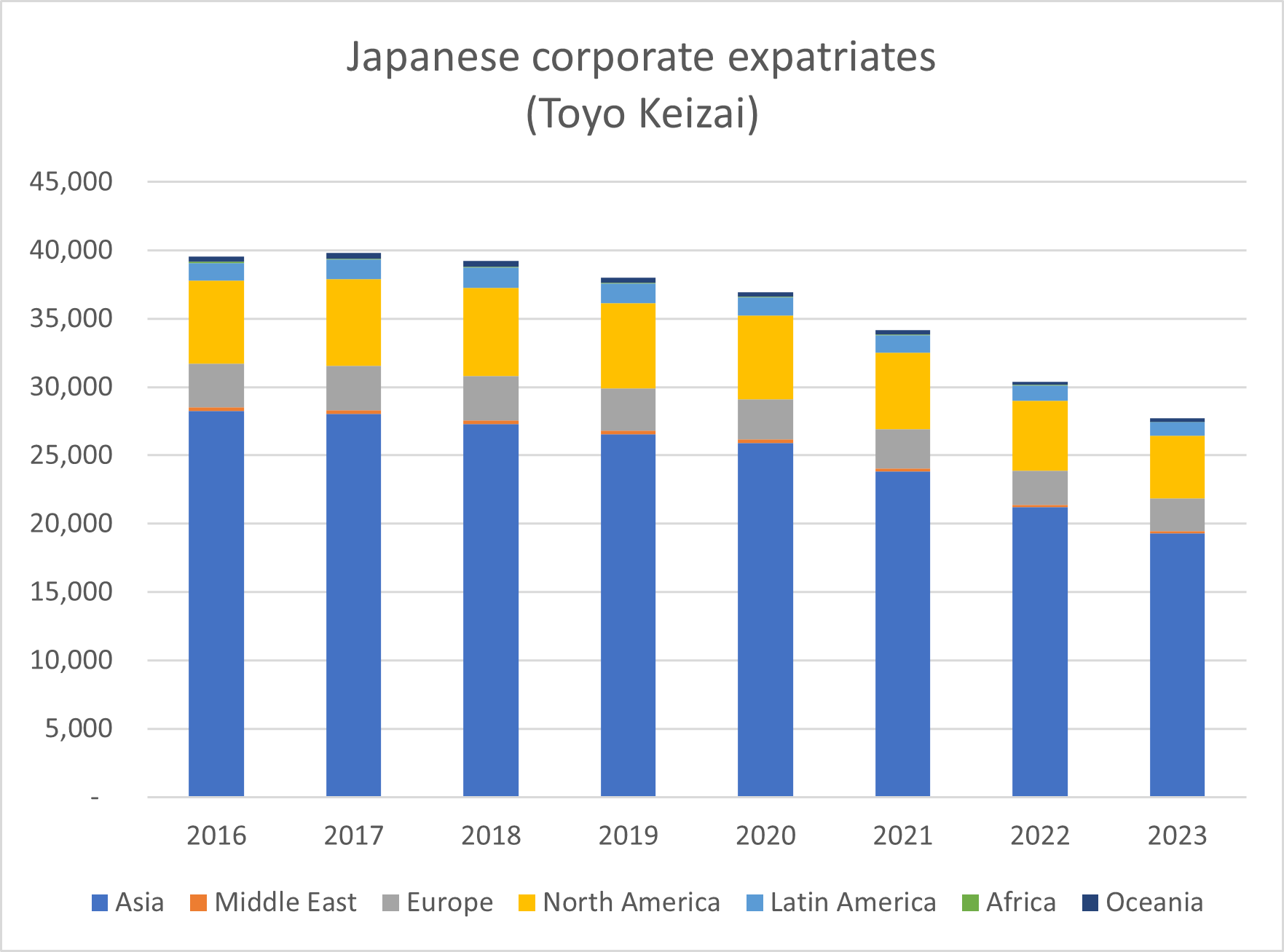 Many other Japanese companies may be adopting similar systems, or just relying more on local managers to run things –
Many other Japanese companies may be adopting similar systems, or just relying more on local managers to run things – 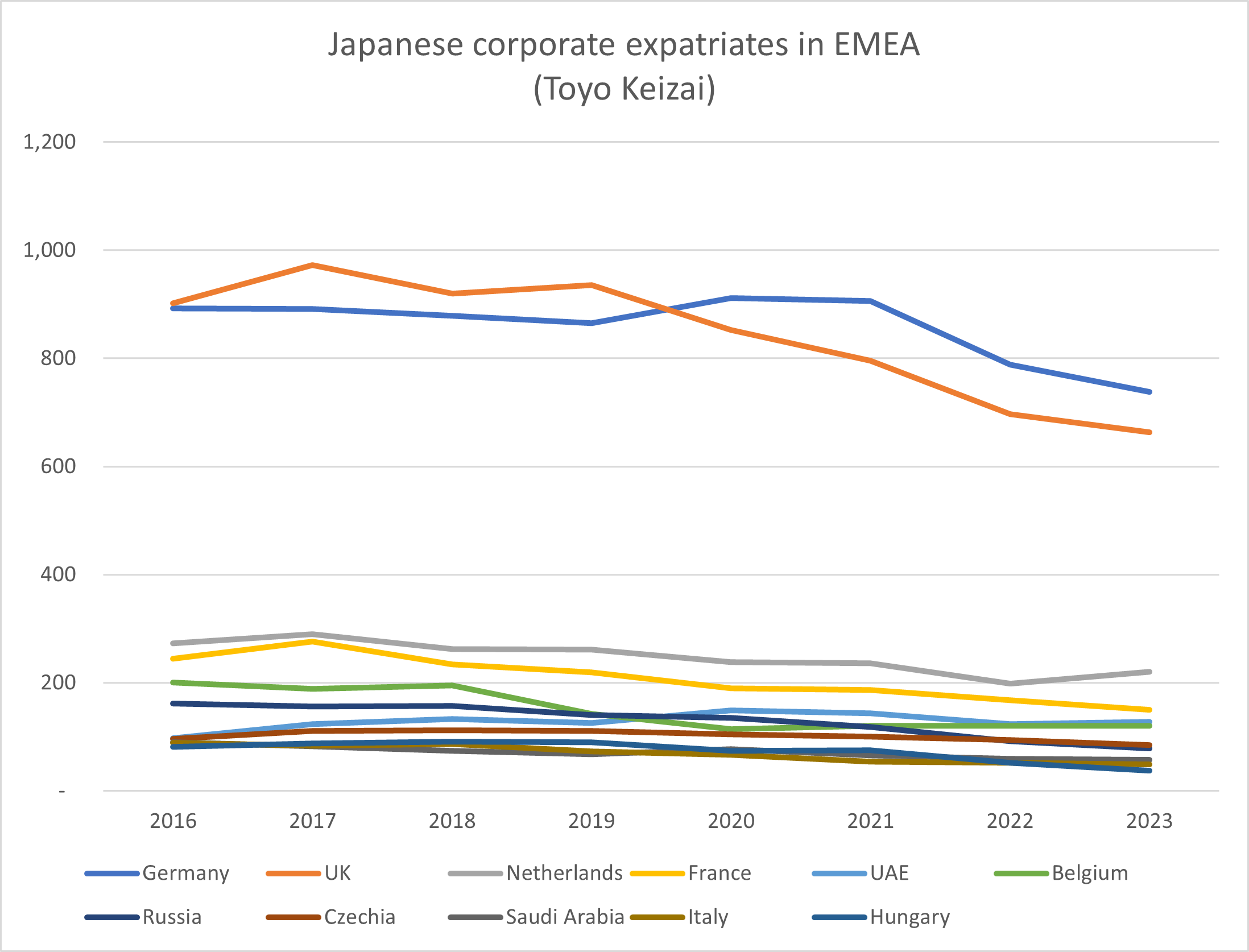 Looking at the Toyo Keizai data for individual countries in Europe and the Middle East shows that the only country to show any positive growth in Japanese corporate expatriate numbers since 2016 is the United Arab Emirates. The fall in Japanese expats in the Netherlands (-19%) was not as steep as elsewhere in EMEA (-27% average, -26% for UK, -40% for Belgium ) and seems to be recovering a bit since the pandemic. The number of expats in Germany also fell by only 17% since 2016, having grown and surpassed the UK in 2019/20, but falling steeply since the pandemic began, with no signs of recovery yet.
Looking at the Toyo Keizai data for individual countries in Europe and the Middle East shows that the only country to show any positive growth in Japanese corporate expatriate numbers since 2016 is the United Arab Emirates. The fall in Japanese expats in the Netherlands (-19%) was not as steep as elsewhere in EMEA (-27% average, -26% for UK, -40% for Belgium ) and seems to be recovering a bit since the pandemic. The number of expats in Germany also fell by only 17% since 2016, having grown and surpassed the UK in 2019/20, but falling steeply since the pandemic began, with no signs of recovery yet.