The annual survey by JETRO of Japanese multinationals shows that many are struggling to return to pre-COVID levels of profitability. 65% of the 7,000 companies surveyed expect to be profitable by the end of FY 2022 (March 31 2023) but the automotive parts sector is forecasting widening losses.
Expectations for profitability are slightly higher in Europe than the global average and within the region, on a country by country basis, business prospects are overall more positive for Japanese companies in the Netherlands and Germany than for those in France or the UK. On the other hand, due to logistics, procurement and energy costs, 35% of Japanese manufacturers in Eastern Europe are expecting their business prospects to worsen, only just balanced out by the 36% who expect their business prospects to improve. Increasing labour costs and hiring and retention even outweigh the impact of the Ukraine war for Japanese companies in Europe as the key challenge. This is also seen as a challenge in Western Europe, but with more focus on white collar, managerial workers, particularly in Germany and the Netherlands.
More than 70% of Japanese companies in the Netherlands, UK, Germany and UAE are expecting to achieve profitability in FY2022. However only 37.9% of companies in the region expect profits to improve, 11.8% lower than 2020/21. More than half of the Japanese companies based in Finland, Ireland, Italy, Sweden, Czech Republic and Portugal are expecting profits to improve – compared to 46.7% of Japanese companies in the Netherlands, 44.4% in the UK, 38.1% in France, 36.4% in Germany, 35.3% in UAE and 31.1% in South Africa. Manufacturers in the UK, having not recovered as quickly as in the rest of Europe from the pandemic, are now more optimistic about profitability for 2022/23 than other manufacturers in the region.
45% of Japanese companies are expecting to expand their business in their region over the next 1-2 years, but do not expect to return to full pre-COVID levels because of rising costs. One bright spot is increasing investment in the human resources and hospitality sectors, thanks to the lifting of coronavirus restrictions.
Within EMEA, more than 50% are expecting to expand their business in Denmark, Portugal, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Ireland and Romania. When asked about expanding “functions”, Germany, UK and the Netherlands were the top 3 for expanding sales functions, Germany, Netherlands and Czech Republic for expanding manufacturing and Germany, France, Spain, UK and Belgium were top for R&D. Overall, particularly for the UK, the mood seems to be “keeping things as they are”
Trade
Over 50% of Japanese companies in the UK say that Brexit has had a negative impact on their business, mainly due to (in rank order) increased customs clearance processes, delays and costs of logistics, imposition of tariffs, responding to new UK regulations (eg the CE vs UKCA mark), customers leaving the UK and difficulties in hiring. 40% of Japanese manufacturers in the UK say they are experiencing problems in exporting to the EU.
37.9% of UK based companies say they are using the EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement for their exports to the EU, 12.9% up on the previous year. The main reason given for not using it was that their exports were already tariff free, or did not fall within the agreement. The main challenges in using the TCA were setting up their own internal systems, getting the cooperation of EU based suppliers or customers and interacting with customs. Securing human resources was cited by 50% of the Japanese companies in the UK as a negative impact of Brexit (61.5% for manufacturers), compared to only 9.8% of Japanese companies in the EU saying they were concerned about this as a result of Brexit.
49% of Japanese companies in the EU are using the EU Japan Economic Partnership Agreement for importing from Japan to the EU and 34% are using the agreement to export from the EU to Japan. More than half of Japanese companies in Austria, Italy, Czech Republic, France and Spain are using the EPA to import to the EU. The sectors with the highest use of the EPA are chemicals, wholesale, foods, plastic products and transportation equipment.
Localization of supply chains and staff
60% of Japanese manufacturers globally are expecting to review their supply chains in the future months. Localization of procurement, production and sales is accelerating due to rising raw material and transportation costs and the emergence of supply chain disruption risks. Within Europe, 48.2% of all companies have reviewed their supply chains and 55.5% expect to review them in the coming year.
In Europe, however, there is more interest in localising procurement within the EU than within the country of location. 21.4% of Japanese companies in Western Europe, 32.1% of Japanese companies in Central and Eastern Europe and only 9.5% of Japanese companies in the UK are expecting to increase domestic procurement, whereas 34.3% of Japanese companies in Western Europe and 45.8% of companies in Eastern Europe are expecting to increase their procurement within the EU. No UK companies are expecting to increase their procurement from the EU and no Eastern European Japanese companies are expecting to increase their procurement from the UK either.
Around 20% of European companies are expecting to increase procurement from Japan, but significantly more (around 35%) are expecting to increase procurement from ASEAN countries.
Japanese companies are also planning to reduce the number of expatriate staff sent from Japan, and increase the number of locally hired staff, particularly in Asia. The pandemic has accelerated the ability to manage the business remotely, from Japan. Within EMEA, 28.9% are expecting to increase their Japanese expats to the Netherlands, compared to a 22.1% increase to UAE, 19.3% increase to Germany, 18.1% to the UK and 13.3% to France and 6.6% to South Africa. 13.3% are expecting to reduce the number of Japanese expats in the Netherlands, 12.4% in Germany, 6.4% to the UK, 16.7% to France.
In terms of hiring more local employees, Japanese companies in Germany came top with 44.3% wishing to do so, then South Africa with 39.5%, Netherlands with 38.9%, France with 37.7%, UK with 36.1%, UAE with 35.9%. 10% of Japanese companies in Germany and the Netherlands were planning to reduce local staff numbers, compared to 11.3% in the UK, 9.8% in France, 9.3% in South Africa, and 4.9% in the UAE.
Whereas automation and reduction of the workforce had been a top priority for manufacturers before 2020, while this is still at number 2, the top priority for the next few years is investment in new equipment and new projects. The third highest priority is revising manufacturing location. The reasons underpinning these priorities are the need to optimise production costs, the high cost of labour and the high cost of raw materials.
CSR and supply chains
A third of Japanese multinationals are doing due diligence on human rights in their supply chains, particularly in Europe, where regulations are being introduced. 46.2% of Japanese companies in the UK are already doing due diligence – compared to 42.9% in France, 30.3% in Germany and 23.2% in the Netherlands. Sectors which are particularly concerned with human rights are mining and minerals, plastic products, non ferrous metals, textiles, construction and foods.
42.4% of Japanese multinationals have started taking steps to reduce their carbon emissions, 9% up on the previous year. 20% of Japanese companies are proceeding with “green procurement” for their suppliers. Portugal, Switzerland, Ireland, Austria, Spain and France score particularly highly in terms of taking steps to reduce carbon emission with over 70% of companies in those countries already having done so, compared to 63.6% in South Africa, 58.3% in the UK, 55.2% in the Netherlands, 51.5% in UAE and 50% in Germany.
Actions taken include reducing energy usage, using more electric power, using more renewable or new energy sources, with solar being the most popular. Other actions have included developing new environmentally friendly products, green procurement and revising procurement and logistics. The interest in green investments is at a record high, greater than digital investments or eco friendly transportation or tourism.
Sales
The most promising sales destination for Japanese companies in Europe continues to be Poland, for the fourth year running. Turkey has overtaken Germany for the first time in 7 years and the UK is back in the top 10. Other Eastern European countries in the top 10 are Hungary, Czech Republic and Romania – mainly for their economic growth prospects. The other Western European countries in the top 10 are France, Italy and Spain.
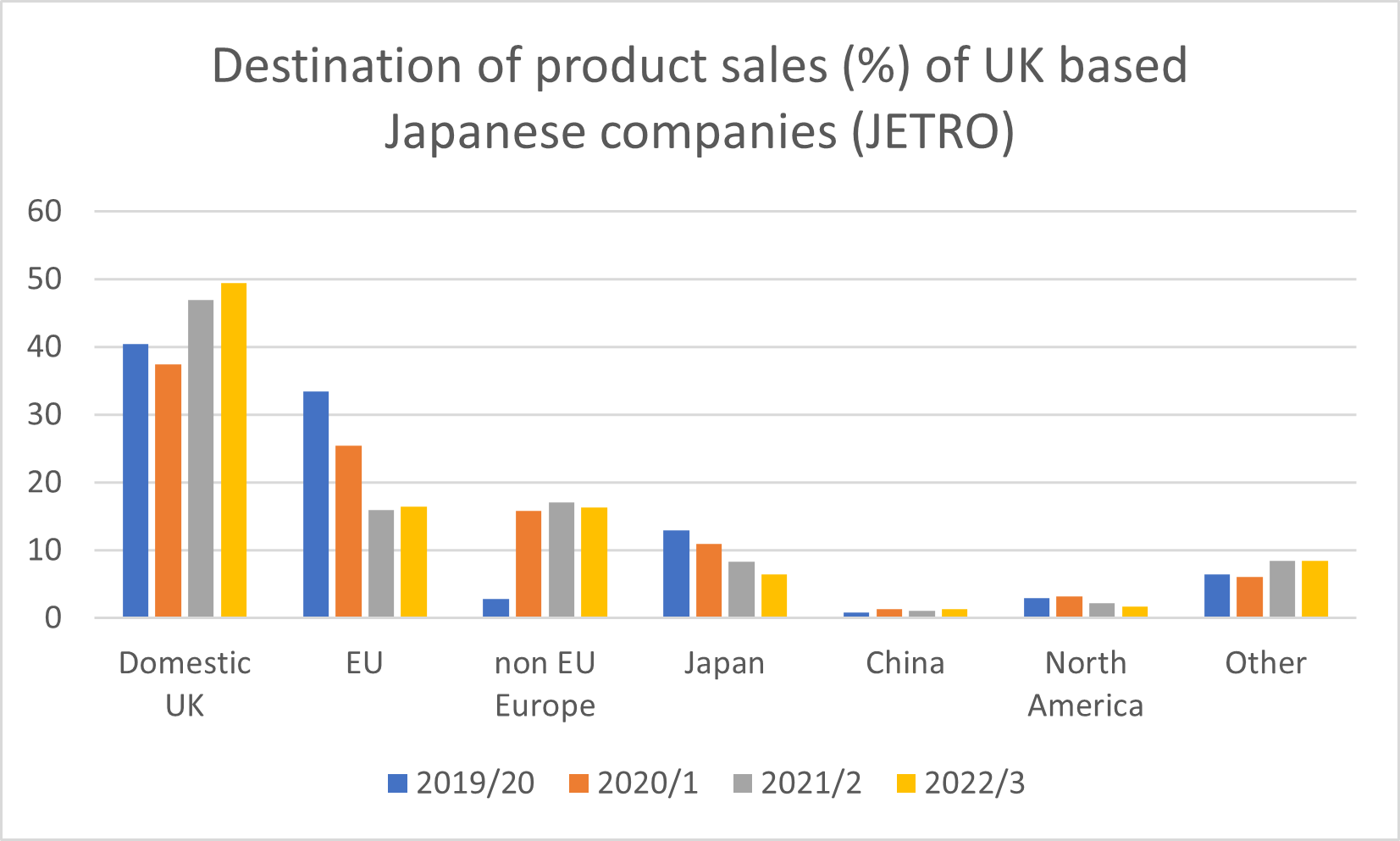 Japanese companies in the UK are showing an increasing focus on the UK domestic market for their sales, with an average of 49.4% of sales to the UK market, 2.4% up on 2021/2, compared to a European average of domestic sales of 37.7%. UK companies are selling on average 16.5% of sales to EU countries, compared to 37.6% of sales to other EU countries (excluding their own country) for Japanese companies located in the EU. Unsurprisingly, Japanese companies in the UK have become more UK oriented since Brexit, as many of the EU sales and coordination functions have shifted from the UK to the EU – and is now potentially stabilising after the sharp decline over 2019/20 to 2021/2
Japanese companies in the UK are showing an increasing focus on the UK domestic market for their sales, with an average of 49.4% of sales to the UK market, 2.4% up on 2021/2, compared to a European average of domestic sales of 37.7%. UK companies are selling on average 16.5% of sales to EU countries, compared to 37.6% of sales to other EU countries (excluding their own country) for Japanese companies located in the EU. Unsurprisingly, Japanese companies in the UK have become more UK oriented since Brexit, as many of the EU sales and coordination functions have shifted from the UK to the EU – and is now potentially stabilising after the sharp decline over 2019/20 to 2021/2
Although the proportion of sales to non-EU Europe (presumably Norway, Switzerland, maybe Turkey) is higher for the UK (16.3%) than for Europe overall (4.4%), there is not much evidence that the UK is being used as a base for sales outside Europe – the proportion of sales to North America (1.7%) or China (1.3%) is actually slightly lower than for the whole of Europe. Sales to Japan have been falling steadily since 2019 (possibly related to Honda Civic sales to Japan). The proportion of sales to “other” countries is higher – 8.5% compared to 6.5%, perhaps showing that some Japanese companies in the UK are indeed Europe, Middle East and Africa headquarters, with sales focused more on the latter regions. ASEAN only accounted for 1% of the 7% of sales to other countries in 2019/20.
Hybrid working and pay rises
European employees of Japanese companies are not returning to the workplace at anything like the rate they are in South West Asia, North West Asia or ASEAN. During 2021, 14.6% of Japanese companies in Europe said that 90% or more of their employees were working at their office or factory and only 29.6% were expecting this to happen in 2022/3 in Europe. In Asia, around 30% of companies said their over 90% of employees were working at the office or factory in 2021 and this is expected to be near to 70% in 2023. This may reflect that there are proportionately more manufacturing companies in Asia than in Europe.
In terms of reviewing management and personnel policies and structure, by far the most popular choice for review was human resource development and training – chosen by 61.6% of Japanese multinationals. Second was reviewing working from home policies, at 35.3%, closely followed by reviewing staff remuneration at 32.3%. The next three topics were all chosen by around 27% of Japanese companies – digitization of workflows, reviewing the expat staff structure and localising management.
Pay rises are highest in emerging markets such as Brazil, India, Mexico, Vietnam and South Africa and in Europe – Hungary, Poland, Romania and Czech Republic – at around 6 to 9% over the past two quarters, whereas despite the high inflation rates, pay is only expected to rise by 2.7% to 4.6% in the Netherlands, Germany, UK, France and UAE.
Update – this article has been added to since the publication of a European focused version of the survey by JETRO in December 2022.
For more content like this, subscribe to the free Rudlin Consulting Newsletter. 最新の在欧日系企業の状況については無料の月刊Rudlin Consulting ニューズレターにご登録ください。
